As artificial intelligence continues to advance, AI generation technology has become a valuable tool in the creative industries. Creators, like scriptwriters and copywriters, now face a crucial decision: should they use advanced AI models to inspire and enrich their creative processes?
A recent study published in Science Advances offers a nuanced answer to this question. While AI has the potential to significantly boost individual creativity, it might also contribute to increased mediocrity and less originality in creative output. These findings shed light on both the benefits and risks of incorporating AI into creative writing, enriching our understanding of how large model applications could influence human behavior and shape the broader social and cultural landscape.

▷ Doshi, Anil R., and Oliver P. Hauser. "Generative AI enhances individual creativity but reduces the collective diversity of novel content." Science Advances 10.28 (2024): eadn5290.
1. Question: How to Assess Creativity?
Generative AI technology is now capable of producing content that appears creative in text (e.g., ChatGPT), images (e.g., Midjourney), audio (e.g., Jukebox), and video (e.g., Pictory). While previous research has shown that AI can collaborate with humans to develop storylines, whether this collaboration truly sparks inspiration or merely confines the creator's thinking to the examples provided by the AI, thereby limiting creative expression, remains relatively unexplored.
When assessing creativity, we typically consider two dimensions: novelty and usefulness. Novelty refers to how much an idea deviates from conventional expectations, indicating a story's originality and uniqueness. Usefulness, on the other hand, concerns how well an idea aligns with intended goals, including the story's adaptability to its target audience, its potential to evolve into a series (e.g., books), and its commercial viability.
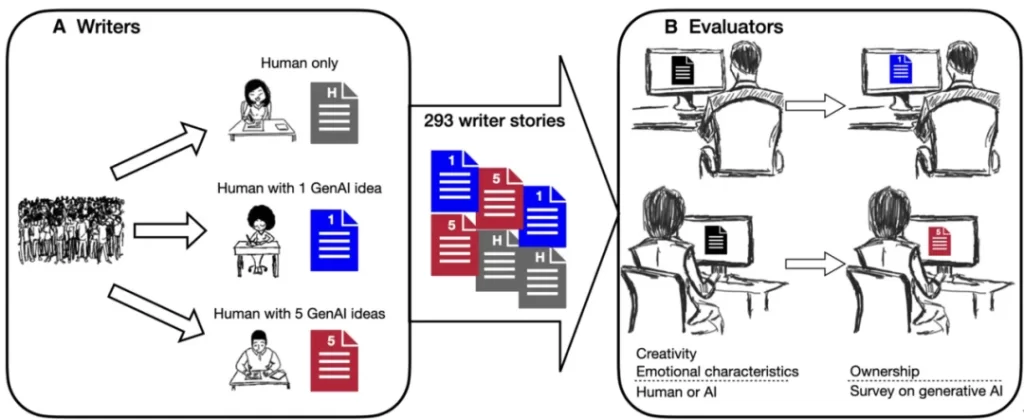
▷ Fig.1. Experimental design flowchart, source: the paper.
In this study, the researchers recruited 293 online participants and asked them to write a brief story consisting of eight sentences. To explore the impact of large models on creative writing, participants were randomly assigned to one of three groups: a human-only group with no AI prompts, a group that received a single AI-generated idea, and a group that received five AI-generated ideas. To assess the creativity of these stories, the researchers recruited an additional 600 evaluators online. These evaluators, unaware of the stories' sources, scored them based on usefulness, novelty, and several emotional dimensions.
2. Findings: Increased Individual Creativity but Decreased Group Diversity
The study found that AI-generated ideas can act as a springboard for human thought, offering starting points that inspire diverse story developments and create a "tree-like structure." Participants who received five prompts from large models showed the greatest creative boost compared to those without AI prompts, with their stories scoring 8.1% higher in novelty and 9% higher in usefulness (Fig.2A).
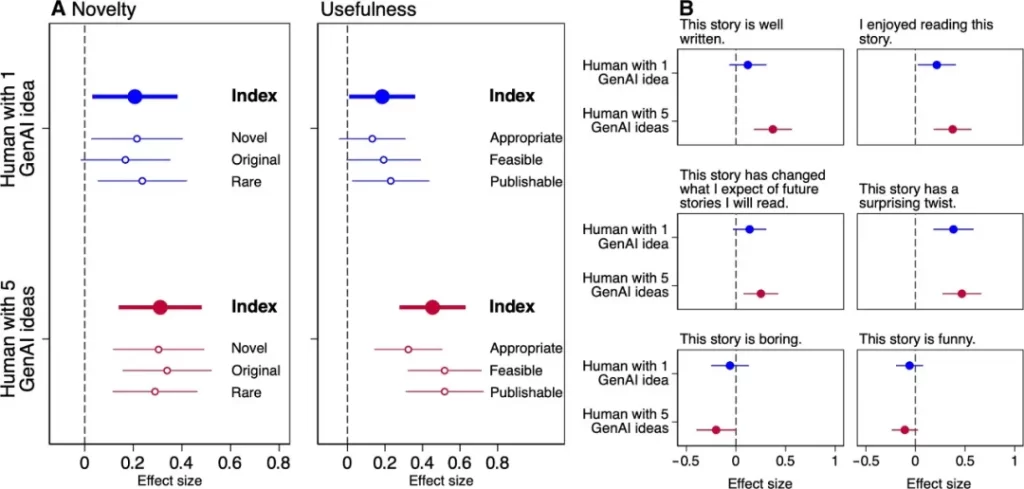
▷ Fig.2. Comparison of the average evaluation results between human writing without large model assistance (baseline) and the groups that received one or five AI-generated ideas.
To assess intrinsic creativity, the researchers had participants complete a divergent thinking task—listing 10 distinct words—before writing. The study revealed that AI-generated ideas had little impact on participants who were already highly creative. However, for those with lower creativity, AI assistance significantly reduced the monotony in their work, lowering it by 15.2%.
The researchers used text embeddings from OpenAI to calculate the similarity between stories. The results showed that stories from participants who received AI prompts were 10.7% more similar to each other, with less variation and diversity. This suggests that while AI assistance can enhance individual creativity, it may also lead to greater similarity among ideas at the group level, reducing collective novelty and diminishing creative diversity.

▷ Fig.3. Comparison of intergroup story similarity among the three groups and the probability density distribution of similarity to AI-generated prompts. A sharper peak indicates higher within-group similarity.
3. Discussion
Interestingly, a paper published in Scientific Reports this February examined GPT-4's divergent thinking in terms of fluency, originality, and elaboration, and found results similar to our study. GPT-4 outperformed human participants on all measures of divergent thinking. When controlling for response fluency, GPT-4 particularly excelled in originality and elaboration. However, compared to humans, GPT-4 used a higher frequency of repeated words and had a more concentrated vocabulary. This finding aligns with the reduction in collective novelty observed in our study.
 ▷ Hubert, K.F., Awa, K.N. & Zabelina, D.L. The current state of artificial intelligence generative language models is more creative than humans on divergent thinking tasks. Sci Rep 14, 3440 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-53303-w
▷ Hubert, K.F., Awa, K.N. & Zabelina, D.L. The current state of artificial intelligence generative language models is more creative than humans on divergent thinking tasks. Sci Rep 14, 3440 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-53303-w
How do large models impact unique human traits like creativity? Current research clearly shows that while AI-assisted creative writing can enhance individual creativity, it also poses a critical risk: the novelty of collective creativity may be compromised. If the publishing industry increasingly embraces AI-generated content, it may become homogenized, leading to a loss of individual creators' uniqueness. This could create a vicious cycle: as individual writers perceive AI-assisted writing enhances their creativity, they may rely more on such technology, potentially weakening overall innovation in literary works.
Of course, the current experimental design has its limitations. The researchers only recruited non-professional writers as volunteers through an online platform, without offering additional financial incentives. Participants who received AI prompts were given those generated by a template, rather than having the freedom to interact with ChatGPT directly. The writing task was limited to composing a short, eight-sentence story that didn’t require complex causal relationships, which doesn’t fully reflect real-world creative writing. Additionally, since this study is based on a Western cultural context, its applicability to Chinese culture remains uncertain.
In summary, while AI holds immense potential for the creative industries, balancing its advantages and disadvantages to ensure healthy technological development will be a significant challenge. Now that you know the results of this experiment, what choice will you make?